Hepatitis B is an infection that attacks the liver. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus and is transmitted through contact with the blood or other bodily fluids of an infected person, including through sexual contact, sharing needles, or from mother to baby at birth.
An acute infection occurs within the first six months after exposure to the virus. Some people may have a mild illness with few or no symptoms, while others have more serious illness requiring hospitalizations or even resulting in death. Most healthy adults can get rid of the virus on their own without treatment.
Chronic hepatitis B occurs when the acute infection has lasted for more than six months. Hepatitis B can be prevented through vaccination – offered in grade seven and to those at high risk of infection.
Local Information
2024 Statistics
Incidence rate is the number of new cases of disease divided by the number of persons at risk for the disease during a particular time period.
Cases:
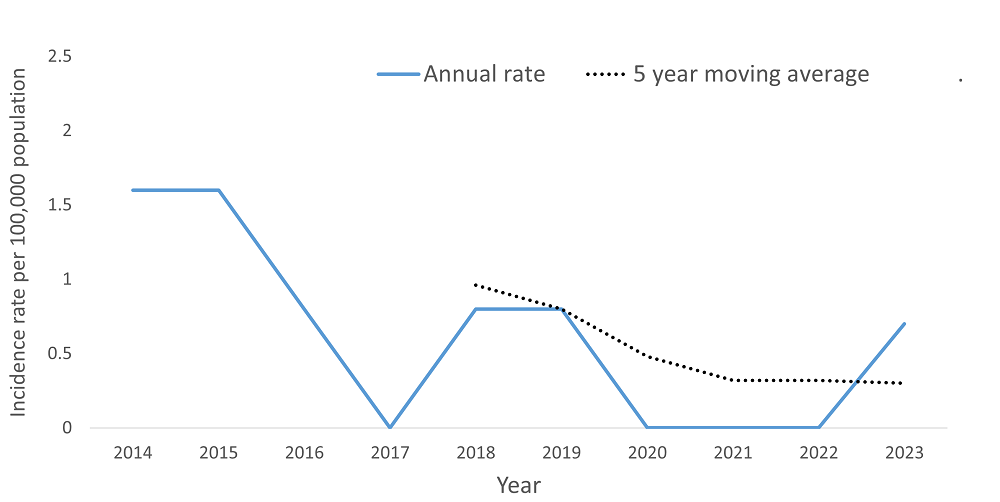
0*
*Includes confirmed Hepatitis B, acute cases in 2024.
Incidence rate per 100,000 in 2024: 0
Incidence rate per 100,000 of Hepatitis B, acute by year
Cases:
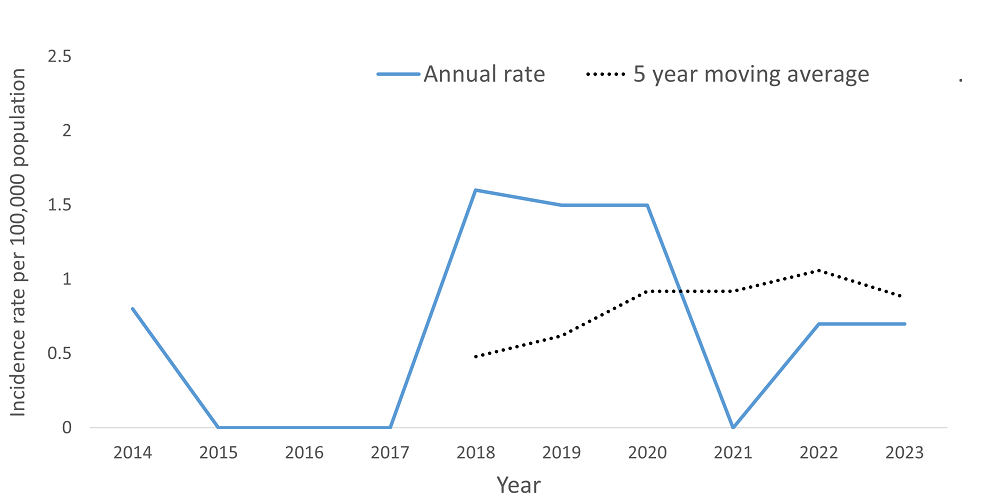
3*
*Includes confirmed cases of Hepatitis B, chronic in 2024.
Incidence rate per 100,000 in 2024: 2.1
Incidence rate per 100,000 of Hepatitis B, chronic by year
Data Sources |
|
More Information about Hepatitis B |
Reporting |
| Report to the Health Unit by next business day by phone at 705-474-1400 or toll free at 1-800-563-2808, ext. 5229 if hepatitis B is suspected or confirmed as per Ontario Regulation 135/18 and amendments under the Health Protection and Promotion Act, R.S.O., c.H.7. |
Should one go to childcare, school, or work if they have hepatitis B? |
|
No exclusion necessary unless too ill to participate in regular activities. Children with hepatitis B and who have no behavioural or medical risk factors, such as unusually aggressive behaviour (e.g., frequent biting), generalized dermatitis, or a bleeding problem, should be admitted to childcare without restrictions. Children with hepatitis B and these behavioural or medical risk factors should be assessed on an individual basis by the child's physician, in consultation with the childcare staff.* Follow the direction of your healthcare provider, public health case manager, or occupational health at your workplace. Note: Exclusion guidelines may differ for healthcare workers. *American Academy of Pediatrics. [Hepatitis B]. In: Kimberlin DW, Banerjee R, Barnett ED, Lynfield R, Sawyer MH, eds. Red Book: 2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Disease. American Academy of Pediatrics; 2024 (p. 457). |
Vaccine Information |
| Hepatitis B is preventable by vaccination. Check your vaccination records or call the Vaccine Preventable Diseases program at 705-474-1400 or toll free at 1-800-563-2808, ext. 5252 to book a vaccination appointment or to obtain additional information. |
Healthcare Provider Information |
|
Contact our Communicable Disease Control (CDC) program at 705-474-1400 or toll free at 1-800-563-2808, ext. 5229, or by email at cdc@healthunit.ca for more information.
Last updated: February 2025, by CDC


